Telecom operators reimagining 5G network UK infrastructure with network swapping amid Huawei wind down decision

How are telecom operators across the globe responding to Huawei ban news?
Ever since the announcement of closing down business partnerships with Huawei, the biggest concern aroused amid such tension is the removal of 5G equipment in a shorter time interval across UK networks and when will 5G be available in UK on a large scale?
In an alternative to such a drastic change, companies are shifting their equipment base from Huawei to different companies. For instance, buyers in US are looking for US based companies like Cisco, Qualcomm, or Juniper Networks to get 5G equipment kit. European manufacturers are favouring telecom enterprises like Ericsson in Sweden and Nokia in Finland. British Telecom (BT)’s Openreach division recently went into alliance with Adtran, a US-based firm to buy full-fibre network kit with first set of deliveries to be started in 2021.
The government is planning to make changes in its policy with Huawei. Nevertheless, telecom operators said they need a minimum of five years to extract all the installed equipment in order to avoid service blackouts, spiralling costs and delay in government plans to facilitate users with ultrafast broadband connections in the entire UK. The government is in talks with multiple vendors and will come with a ‘Telecoms Security Bill’ soon.
It seems like Nokia has taken this as an opportunity to fill this technological gap in 5G as it states to replace all of the Huawei equipment in the UK’s networks at scale and speed with its huge capacity and expertise in the telecom domain. Another company that gained advantage from such an action is Ericsson. Many telecom operators are approaching the Swedish company as a substitute for Huawei to replace either the core network or radio access network.
In 2018, Australian government had already banned Huawei for supplying 5G equipment. Originally, it was agreed that Huawei would bring high-speed internet to Papua New Guinea and Solomon Islands, but later on Australia decided to move on with the project funding and building the infrastructure itself. Even New Zealand based largest telecommunications and digital services company, Spark was restricted to use Huawei 5G equipment in this year.
Shifts in Europe can be experienced with the announcement of a contract partnership between Telefónica Deutschland and Ericsson. Huawei has been the major player in 4G technology for most of the telecom providers in Germany. But the current situation made them put an end to their partnership with various Chinese vendors.
Impact of Huawei ban on the telecom industry
-
Telecom operators in UK will experience higher CAPEX as Huawei equipment is banned in the country’s 5G networks.
-
Billions of monies invested on Huawei infrastructure by operators in UK specifically BT and Vodafone may experience huge loss. Since 5G deployment in UK was in its first phase, the ban has reduced equipment pricing competition to provide 5G network services to its subscribers in UK.
-
Lack of interoperability between current 4G and new 5G infrastructure may require total replacement of 4G and 5G equipment from a new vendor incurring more expenses.
-
Such activities involve huge amount of time and will ultimately cause delay in delivery of 5G networks to users and might as well disrupt existing 4G services.
-
People have spent years with high training costs to learn Huawei equipment skills, achieve professional growth and enhance their livelihood. But Huawei UK ban has left them behind and are in a state to rethink their way of surviving this situation.
-
Telecom operators require 5G network swapping to a different 5G equipment from existing Huawei cell towers to provide seamless 5G network services and uninterrupted current 4G services to consumers.
How 5G network swapping affects the users on the network?
All these factors need to be considered while swapping mobile network without its interference in 5G network services to current users:
-
Swapping of networks from 4G and 5G networks can lead to outages, degraded services and network churn deteriorating network experience to users.
-
User experience is key for telecom operators and are constantly working to satisfy their consumer needs. Reinstalling 5G network equipment again becomes a crucial task to facilitate users with 5G connectivity.
-
However, it is critical for operators to transform the network equipment to a new environment with suitable network parameters optimisation to provide enhanced network connection, higher data throughput and, better voice services.
-
Customer engagement can only be increased if these elements are present in a network user experience. Proper planning with a set of strategies should be implemented before going ahead with network swapping to match 5G network requirements in digital era.
Why is 5G Network swapping critical for MNOs?
New-age 5G technology features higher capacity, lower latency and increased bandwidth benchmarked with 4G. As per the research by CB insights, 5G wireless technology has huge impact across verticals like:
-
Manufacturing: 5G technology is enabling manufacturers to leverage automation, Artificial Intelligence, Internet of Things (IoT) to enhance smart factories which is more flexible and efficient with increased safety.
-
Financial Services: Customers nowadays prefer digital platforms to make online payments through their devices. As 5G is facilitating higher speed, banking institutions are relying on it to accelerate digitization and upgraded mobile operations to increase their customer engagement.
-
Healthcare: With increased 5G use cases like remote monitoring with devices like wearable tech, remote robotic surgery in healthcare industry, 5G networks could improve such medical processes and provide better well-being to patients.
These procedures can be executed in the presence of high data throughput connection, low latency, to enable ultra-fast lag-free connections and can be only possible with 5G network connections. This has resulted in huge demand for 5G network connectivity across verticals to increase their efficiency as well as organizational productivity thereby improving the lives of consumers.
MNOs perform 5G network swapping on wired network clusters of computers. As the number of deployments of 5G networks is expanding with the use of new spectrum and latest technologies, MNOs need to evaluate critical infrastructure requirements and redesign network architecture. With network swapping as the main focus for the telecom operators in UK, it is equally important to improve network coverage, higher network capacity, increased data throughputs. Technological expertise will enable operators to deploy cutting-edge technology to give the best voice and mobile data experience to users.
What are the new emerging technologies in the wake of Huawei ban?
The ban has led to an emerging trend where MNOs are adopting Open Radio Access Network (abbreviated as OpenRAN) wireless network architecture that is compatible with existing 4G/3G network infrastructure and also, 5G networks expected to be added in near future. The main idea behind this concept is to increase interoperability between various vendors permitting MNOs mix and match equipment from different suppliers that will eventually curb costs and improve flexibility.
Start-up organizations namely Mavenir, Parallel Wireless, Altiostar are utilizing this opportunity to develop OpenRAN software and keen in doing partnerships with hardware companies to increase their business. They can improve efficiencies solving many problems not just limited to a single service provider.
5G Network Swapping
Challenges
Networks have always been a critical part of many industrial installations. Modern networks can potentially use numerous styles of switching equipment. While network swapping is a critical solution for the Telcos, at the same time it is a herculean task and requires a skilled workforce to handle such workloads. They need to have a proper Radio Network planning as they move forward with the swapping of Huawei equipment to a different vendor.
According to BT, it may cost around £500 million, to remove Huawei equipment under UK government and at least needs five years to accomplish the same.
Requirements
Radio Network planning needs to be done as they are considering 5G network swapping as an option to remove their Huawei equipment to a different equipment vendor. The process involves a huge set of tasks like:
-
Swapping should not affect current services to existing subscribers.
-
Switching off current Huawei equipment to transition it into new equipment for example, Nokia equipment.
-
Reinstallation of 5G cell towers is highly time consuming and may take around five years to complete this task. It requires huge lifting equipment like cranes to hold big cell towers and place it on the exact position of the site. Once this is done, reconfiguration of the existing cell tower with 5G technology is carried out on the newly installed cell towers.
What are the processes and tools required during 5G base station swapping from Huawei to new vendor?
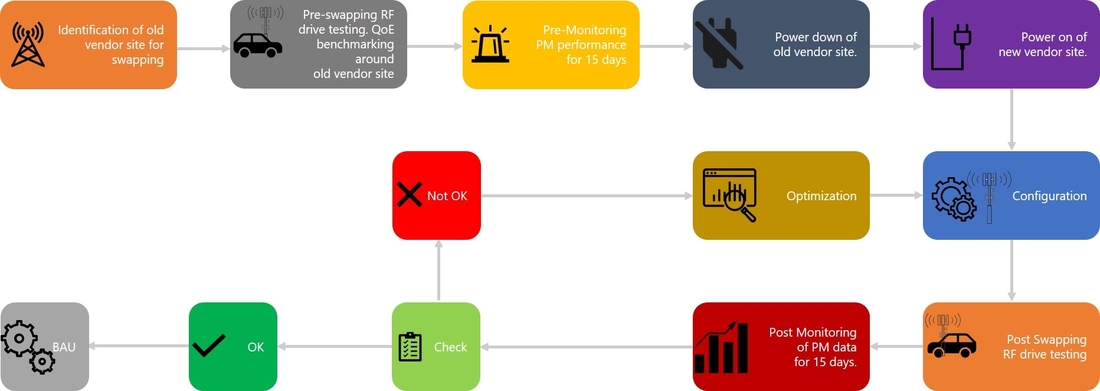
Telecom operators are in the process of 5G network swapping as they are moving forward with pre-swapping and post-swapping measurement methods. They need to assess current performance of Huawei 5G base stations in terms of handover KPIs, throughputs, network assessment. MNOs target ~20-30 locations to swap networks in one day which requires huge investments along with time.
After performing 5G network swapping, telecom operators need to assess the cell tower site for network coverage, improved data speed, voice services and other key KPIs. These can be measured with RF tools in the market like RantCell that can perform walk testing, drive testing to test the swapped 5G base station performance in specific location.
RantCell is an Android-based application that can be easily mass deployed to various teams and conduct network tests to evaluate performance of 5G base station and accelerate 5G swapping.
Conclusion
Though Huawei UK ban has brought certain unavoidable circumstances, a 5G future is still awaiting to transform the telecom industry in UK. With the rise of new 5G use cases across different verticals, demand for 5G will continue to grow in the upcoming years. Telecom operators can capitalize on this opportunity to build industry-specific applications clubbed with new-age technologies like AI/ML, edge computing, Big Data etc. and reap significant benefits meeting Industry 4.0 needs.


